shoulder labrum tear diagnostic test|shoulder labral tests physical therapy : store The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) . See more webPadre Alex Nogueira. @PadreAlexNogueira ‧ 1.96M subscribers ‧ 3.9K videos. Este canal tem a missão de realizar um apostolado, com a divulgação de vídeos da Fé Católica, principalmente na.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 9 de nov. de 2023 · Para muitos que gostam de apostar em esports, a GGBET é um dos nomes que chama mais a atenção. Mas será que vale a .
speed's test vs o'brien's
the boys studied hard to pass the class test
The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) . See moreYour shoulder is a large and complex joint. The O’Brien test focuses on your AC joint and labrum. Your AC joint is one of four shoulder joints, where two bones . See moreHealthcare providers who may perform the O’Brien test include: 1. Athletic trainers. 2. Orthopedists(bone and joint specialists). 3. Physical therapists. 4. . See moreSpecial testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive .
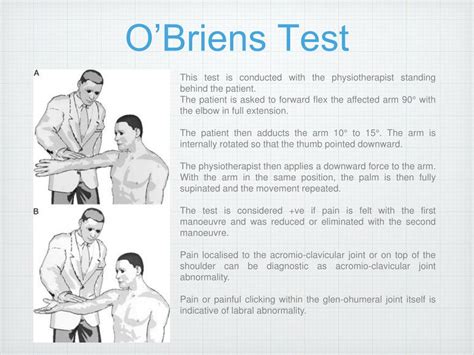
The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] Technique. With the patient in sitting or standing, the upper extremity to be tested is placed in 90° of shoulder .
To evaluate for a possible shoulder labrum tear, a Penn orthopaedic specialist will examine your shoulder, conduct several physical tests to check your range of motion, take a full health history and discuss any past injuries you may have had. Here I demonstrate for you in this video how to perform the O'Brien's Test and talk about what a positive test is and what it means. 👉MedBridge: Online CEUs.The best tests available to make the diagnosis of a labral tear are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram (the latter is a CAT scan preceded by an arthrogram where dye is injected into the shoulder). .O’Brien’s Test is a special orthopaedic/orthopedic test for the shoulder that attempts to test specifically for glenohumeral joint labral tears (and more specifically for SLAP Lesions; .
Shoulder pain is a common complaint in family practice patients. The unique anatomy and range of motion of the glenohumeral joint can present a diagnostic challenge, but a proper clinical .
Here I demonstrate for you in this video how to perform the O'Brien's Test and talk about what a positive test is and what it means. 👉MedBridge: Online CEUs. A shoulder labrum tear is a tear of the labral cartilage that lines the shoulder joint. Get detailed information about labral tears, including SLAP tears and Bankart tears, shoulder labral tear symptoms, diagnostic tests, . There are no diagnostic tests for frozen shoulder. A healthcare provider makes the diagnosis simply by observing how well (or not) you can move the shoulder. . The Crank test is used to identify a labral tear. This is a common injury in .
special tests for shoulder labrum
Rotator cuff tears are common injuries caused by damage to the muscles or tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint. They can be diagnosed by using a number of tests and imaging techniquesThere are several types of labral tears: A SLAP lesion (superior labrum, anterior [front] to posterior [back]) is a tear of the labrum that usually occurs on the upper part of the socket and may also involve the origin, or starting point, of the long head of the biceps tendon.; A tear of the front part of the labrum at the bottom of the socket is called a Bankart lesion.The validity and accuracy of clinical tests used to detect labral pathology of the shoulder-a systematic review. Man Ther. 2009;14(2):119-130. ↑ Dessaur WA, Magarey ME. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for superior labral anterior posterior lesions: a systematic review. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(6):341-352.A SLAP tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion. . Arthroscopy Joint Replacement Preparing for Surgery Nonsurgical Treatments Diagnostic Tests Ortho-pinion Blog .
To assist in the diagnosis of a labral injury, a history and clinical evaluation of the labrum is required. Radiological investigations are very important because these clinical tests have not been demonstrated to have high degrees of accuracy. There are a bewildering array of shoulder tests that supposedly interrogate specific structures.
Providers use the following tests to diagnose SLAP tears and determine treatment: Physical examination. Your doctor will check your arm and shoulder range of motion and strength. . In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. Type 3: Torn labrum tissue is caught in the shoulder joint. Type 4: In this type .This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. . Liu SH, Henry MH, Nuccion S, Shapiro MS, Dorey F. Diagnosis of glenoid labral tears: a comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and clinical examinations .
A tear may also occur from a blow to the shoulder or from a fall. General wear from years of use can also make the shoulder labrum more susceptible to tears. Shoulder labral tears may cause pain in the joint while you are performing overhead activities such as placing items on a shelf or playing sports such as basketball or tennis. You may also . Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of the utmost .Shoulder labrum tears may occur: Within or along the edge of the glenoid labrum: most frequent type of glenoid labrum tear, particularly over the age of 40.May not cause any noticeable symptoms; Where the biceps tendon attaches: at the top of the glenoid labrum Where it attaches to the bone: the labrum may become completely detached and a small fragment of bone may .An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Labral tears cause groin pain or pain in the anterior side of the hip, and less commonly buttock pain. This mechanically induced pathology is thought to result from excessive forces at the hip joint. For example, a tear could decrease the acetabular contact area .
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. Clinically Relevant . A standing radiograph should be the initial imaging test. 24 Previously, magnetic resonance arthrography (1.5 tesla) with gadolinium injection of the hip was the diagnostic standard for labral tears.
stand behind patient, flex elbow to 90°, hold shoulder at 20° elevation and 20° extension. Internally rotate shoulder to near maximum holding the wrist by passively lifting the dorsum of the hand away from the lumbar spine – then supporting the elbow, tell patient to maintain position and release the wrist while looking for a lag.The data for the proposed Bankart lesion/anterior labral tear tests are presented in Table 4. The TIC that includes that crank test, the apprehension test, . as studies with better statistical data emerge for specific special tests and/or categories of shoulder diagnosis. Special testing should, in the author's opinion, simply should be an . A SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and biceps tendonitis.SLAP Lesion Cluster 1 | Shoulder Assessment. According to a study done by Schlechter et al. (2009), a combination of the Active Compression Test and the Passive Distraction test yields a positive likelihood ratio of 7.0 for 2 positive tests and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.33 for two negative tests. This test cluster therefore has moderate clinical value to confirm or rule out .
Rosas et al. (2017) have conducted a literature review and have come up with a test cluster. They found that the uppercut test combined with tenderness to palpation of the long head of the biceps had the highest accuracy to diagnose pathology of the proximal biceps with a sensitivity of 88.3% and a specificity of 93.3%. Although accuracy seems to be high, this combination has not been .MRI and MRA are considered the gold standards for the diagnosis of labral tears; therefore, a comparison of the five special tests identified was made to these two medical image studies. . The results of the current study indicate that a combination of at least three or more positive clinical tests for a shoulder labral tear may be used to . Introduction. Snyder et al. 1 first coined the term SLAP (superior labrum anterior to posterior) lesion in 1990 after identifying the specific pattern of injury to the superior labrum of the shoulder arthroscopically in 27 patients with various shoulder disorders. A SLAP lesion is an injury to the fibrocartilage rim that runs along the margin of the glenoid cavity. 2 Because of . Superior labral anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions constitute a recognized clinical subset of complex shoulder pain pathologies. SLAP lesions demonstrate a predilection for young laborers, overhead athletes, and middle-aged manual laborers.[1] In 1985, Andrews first described superior labral pathologies, and Snyder later coined the term “SLAP lesion” because of the .
Mechanical block: labral pathology, frozen shoulder (see MRI image to the right) Night pain (lying on affected shoulder): rotator cuff pathology, anterior shoulder instability, ACJ injury, neoplasm (particularly unremitting) Sensation of ‘clicking or clunking’: labral pathology, unstable shoulder (either anterior or multidirectional . Background: Physical examination tests of the shoulder (PETS) are clinical examination maneuvers designed to aid the assessment of shoulder complaints. Despite more than 180 PETS described in the literature, evidence of their validity and usefulness in diagnosing the shoulder is questioned.

WEBr/Famosas18: CONTEÚDOS DAS MODELOS MAIS GATAS DO BRASIL,Não autoriza a publicação? Entre em contato com os administradores que excluiremos. +18 PARA.
shoulder labrum tear diagnostic test|shoulder labral tests physical therapy